© 2023 yanghn. All rights reserved. Powered by Obsidian
7.1 深度卷积神经网络(AlexNet)
要点
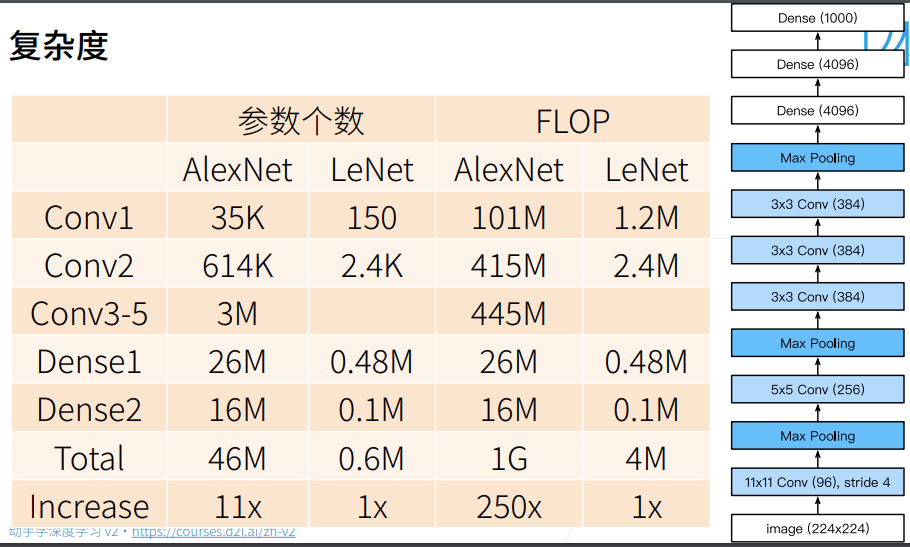
- AlexNet 是一个更大更深的 LeNet,10 倍参数、260 倍计算量
- 新引入丢弃法、ReLU、最大池化层和数据增强
- 尽管 AlexNet 的代码只比LeNet多出几行,但学术界花了 20 年(2012)才接受深度学习这一概念,再此之前都是研究图像特征
1. 计算机硬件、数据与学习算法发展
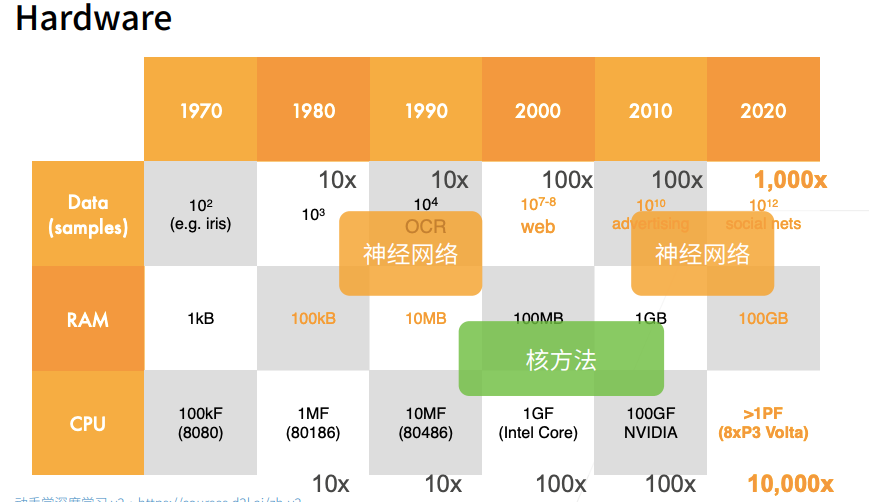
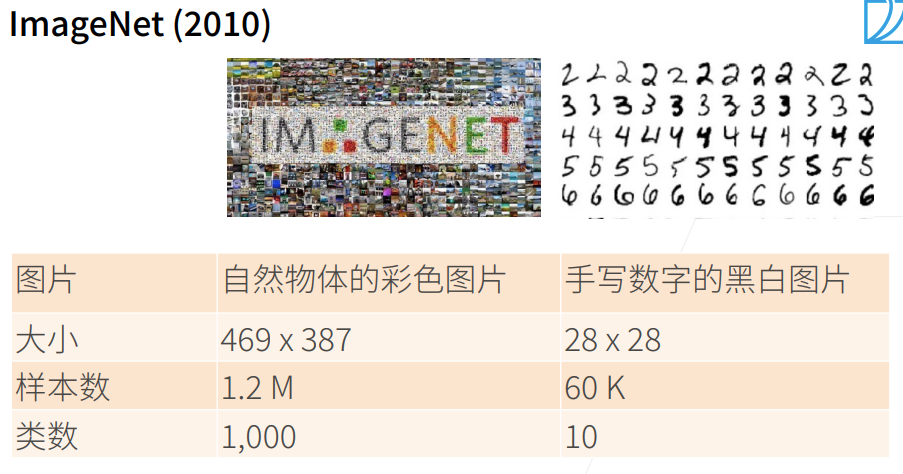
- AlexNet 赢得 2012 年 ImageNet 竞赛冠军
- 更深更大的 Lenet
- 主要改进:
- 丢弃法 4.6 Dropout
- 从 Sigmoid 改成 Relu(Sigmoid 容易出现梯度消失,因为 Sigmoid 最大梯度是 0.25 4.1 多层感知机 MLP#^d21fc2)
- MaxPooling
- 数据增强(将图片翻转、裁切和变色等处理)
- 计算机视觉方法论的改变(从焦距图像特征抽取到更深更大的网络)
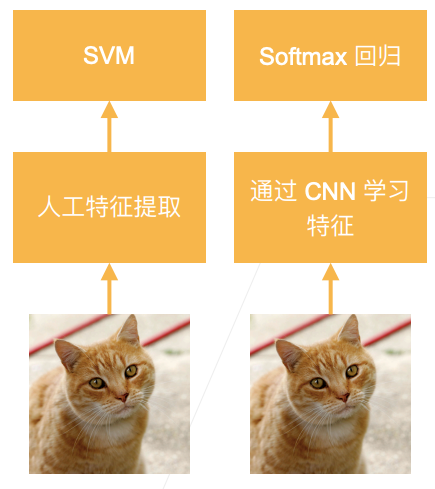
2. AlexNet
2012年,AlexNet 横空出世。它首次证明了学习到的特征可以超越手工设计的特征。它一举打破了计算机视觉研究的现状。 AlexNet 使用了8层卷积神经网络,并以很大的优势赢得了2012年 ImageNet 图像识别挑战赛
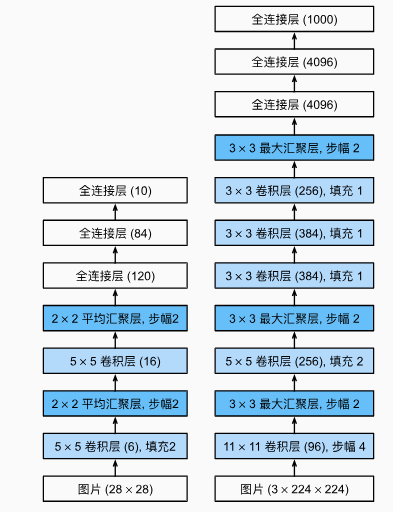
与 6.6 卷积神经网络(LeNet) 相比,输入图片变得更大,这样卷积核的大小也要变得更大,左后用了很大的全连接层
3. 实现
import torch
from torch import nn
from d2l import torch as d2l
net = nn.Sequential(
# 这里使用一个11*11的更大窗口来捕捉对象。
# 同时,步幅为4,以减少输出的高度和宽度。
# 另外,输出通道的数目远大于LeNet
nn.Conv2d(1, 96, kernel_size=11, stride=4, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 减小卷积窗口,使用填充为2来使得输入与输出的高和宽一致,且增大输出通道数
nn.Conv2d(96, 256, kernel_size=5, padding=2), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
# 使用三个连续的卷积层和较小的卷积窗口。
# 除了最后的卷积层,输出通道的数量进一步增加。
# 在前两个卷积层之后,汇聚层不用于减少输入的高度和宽度
nn.Conv2d(256, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 384, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Conv2d(384, 256, kernel_size=3, padding=1), nn.ReLU(),
nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2),
nn.Flatten(),
# 这里,全连接层的输出数量是LeNet中的好几倍。使用dropout层来减轻过拟合
nn.Linear(6400, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
nn.Linear(4096, 4096), nn.ReLU(),
nn.Dropout(p=0.5),
# 最后是输出层。由于这里使用Fashion-MNIST,所以用类别数为10,而非论文中的1000
nn.Linear(4096, 10))
打印一个样本在模型各层的输出:
X = torch.randn(1, 1, 224, 224)
for layer in net:
X=layer(X)
print(layer.__class__.__name__,'output shape:\t',X.shape)
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 54, 54])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 54, 54])
MaxPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 96, 26, 26])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 26, 26])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 26, 26])
MaxPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 12, 12])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 384, 12, 12])
Conv2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 12, 12])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 12, 12])
MaxPool2d output shape: torch.Size([1, 256, 5, 5])
Flatten output shape: torch.Size([1, 6400])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
ReLU output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Dropout output shape: torch.Size([1, 4096])
Linear output shape: torch.Size([1, 10])
读取并训练数据:
batch_size = 128
train_iter, test_iter = d2l.load_data_fashion_mnist(batch_size, resize=224)
lr, num_epochs = 0.01, 10
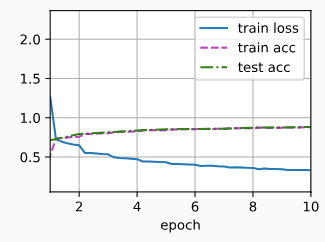
d2l.train_ch6(net, train_iter, test_iter, num_epochs, lr, d2l.try_gpu())
loss 0.331, train acc 0.878, test acc 0.883
3941.8 examples/sec on cuda:0